Introduction
We’ve seen artificial intelligence revolutionizing every dimension of modern-day healthcare. And nursing care isn’t left untouched by the marvels of it. Artificial intelligence in nursing is bringing in new, innovative ways of work that are assisting nurses in:
- Patient monitoring
- Medication management
- Real-time care decisions
Long story short, with AI, nurses aren’t finding themselves knee-deep in redundant work and are having more time and space to focus on critical, hands-on care.
In the next ten minutes, we’ll discuss how AI agents are transforming nursing care. We’ll talk at length about the role, benefits, and applications of artificial intelligence in nursing, and what the future looks like for nurses and care providers who are still trying to adapt to the winds of change.
Understanding AI Agents in Nursing
In nursing, AI agents are virtual assistants built on generative LLMs (say ChatGPT or DeepSeek) that handle everyday patient communication and routine tasks.
These agents answer common health questions, schedule and manage appointments, and remind patients about their medications. This gives nurses more breathing room to focus on the more complex, human side of care.
What makes these nursing AI agents loved is how they just don’t spit out scripted answers, but understand patient context, process natural language in real time, and respond with personalized guidance. Instead of bluntly saying, “You missed your dosage,” an AI agent might frame it with care: “Looks like you’ve missed your meds a few times. Let’s fix that. I’ll set up a daily reminder calendar so it’s easier to stay on track.”
In other words, they act like humans. They listen, understand, and proactively respond, whether it’s calming a nervous patient before surgery or simply checking in to ask how recovery is going.
Besides the scenes, AI agents take on the admin load, from charting, documentation, and appointment coordination. They step in for triage and remote monitoring too, spotting early warning signs before they turn serious. And because many can communicate in multiple languages, they make care more inclusive, reaching patients regardless of their background or ethnicity.
The AI agent market is currently booming, projected to hit about $7.6B in 2025. With the healthcare industry facing a massive nursing shortage, having these context-aware AI agents have become instrumental to keep workflows going smoothly.
Applications of AI Agents in Nursing Practice
Wherever you’re in your healthcare transformation journey, AI agents have the potential to take that transformation to a new level. Let’s explore the top use cases of AI agents in nursing care and how the industry landscape is shifting for good.
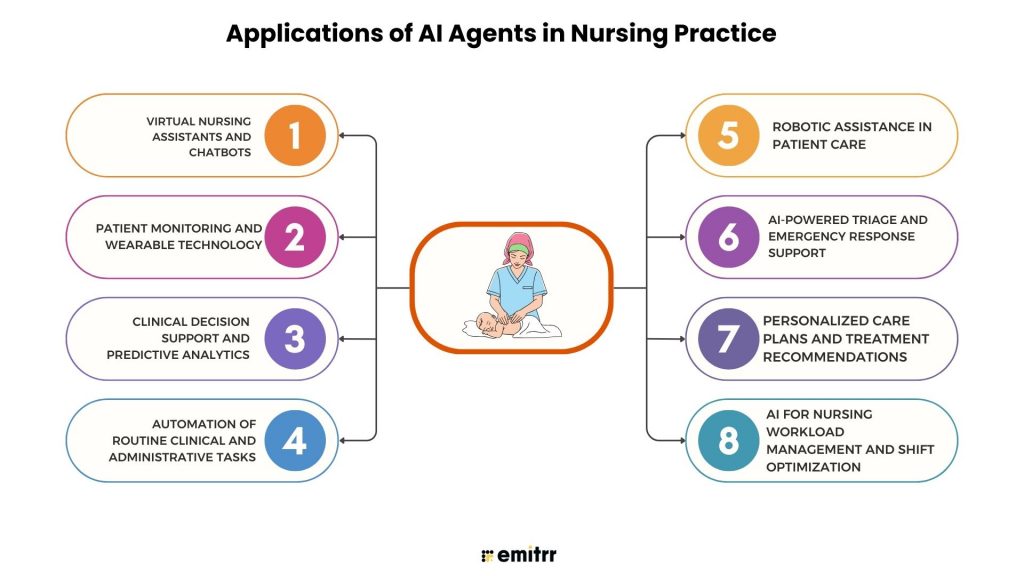
1. Virtual Nursing Assistants and Chatbots
AI chatbots and voice assistants step in as the first line of patient contact. They answer common health questions, triage low-risk symptoms, and manage scheduling of patients, all while understanding the natural language in real time. These agents have multilingual capabilities, making care more accessible and inclusive across diverse populations. Leveraging the power of artificial intelligence in healthcare, clinics use these agents to collect pre-visit information, push tailored education, and hand off complex tasks to humans.
2. Patient Monitoring and Wearable Technology
Wearables have moved far from being fitness accessories. These have become healthcare vitals, ensuring care despite distance, mobility limits, or the unpredictability of hospital visits. From smart rings to hospital-grade sensors, wearables stream patient data into AI agents in real time, making it entirely possible for nurses to have their fingertips right at the patients’ pulse. Instead of nurses combing through endless charts, these AI agents can process data, spot subtle changes, and raise alerts before issues escalate.
3. Clinical Decision Support and Predictive Analytics
AI agents sift through EHR data and flag near-term risks, giving nurses the much-required, timely, and evidence-backed nudges before things take an ugly turn. These agents tap into the data in less than a second, identify anomalies, and help care teams prioritize rounds and preempt crises rather than react to them. These predictive insights act as a major contributor to improved care outcomes, spotting early sepsis risks, highlighting drug interactions, or predicting readmission chances.
4. Automation of Routine Clinical and Administrative Tasks
Charting. Scheduling. Prior authorization. Documentation. These repetitive, tedious chores used to eat up hours every shift. AI agents, however, have come to the surface as a key multiplier of productivity, drafting clinical notes, pushing billing updates, and auto-filling forms in seconds. An absolute win-win for nurses! For them, it isn’t just about saving time; it’s about reclaiming the headspace to connect souls with care and take care of their patients with complete focus.
5. Robotic Assistance in Patient Care
With the influx of artificial intelligence in healthcare, robots are no longer a fragment of imagination. In busy wards, AI agents are useful in carrying supplies, delivering meds, and even repositioning patients. That means fewer strained backs, fewer wasted steps, and more time for direct bedside care. Some companion agents also provide social support for long-term patients—keeping spirits up while nurses juggle heavier clinical duties.
6. AI-Powered Triage and Emergency Response Support
Emergency departments can feel like organized chaos. That’s where AI agents jump in. They sort patients by urgency, guide ambulance dispatches, and make sure beds and staff go where they’re needed most. The result is faster triage, shorter wait times, and critical cases getting attention without delay.
7. Personalized Care Plans and Treatment Recommendations
Care has never been one-size-fits-all, and AI agents make sure it doesn’t feel that way anymore. They dig into a patient’s health records, test results, lifestyle habits, and even genetic markers to suggest highly tailored care plans. Nurses then refine those plans with the empathy and intuition only humans can offer. What you get is the best of both worlds: precision from AI, compassion from nurses.
8. AI for Nursing Workload Management and Shift Optimization
Scheduling in nursing has always been messy. AI agents now smooth that out by predicting demand, balancing shifts, and respecting nurse preferences when possible. The effect goes beyond neat rosters. Teams feel less stretched, morale improves, and patients benefit from safer, more consistent care. For an industry fighting burnout, this shift feels less like innovation and more like survival.
Save time with ready-to-use voicemail greetings for nursing teams. Download and start using them instantly.

Benefits of AI Agents in Healthcare and Nursing
AI agents in healthcare are that quiet layer of intelligence, making the impossible workload feel a little lighter and assisting nurses in more ways than one.
If you’re struggling to navigate healthcare workflows – and wondering how AI agents can benefit your establishment – this section that covers the benefits of AI in healthcare is something you must glean on.
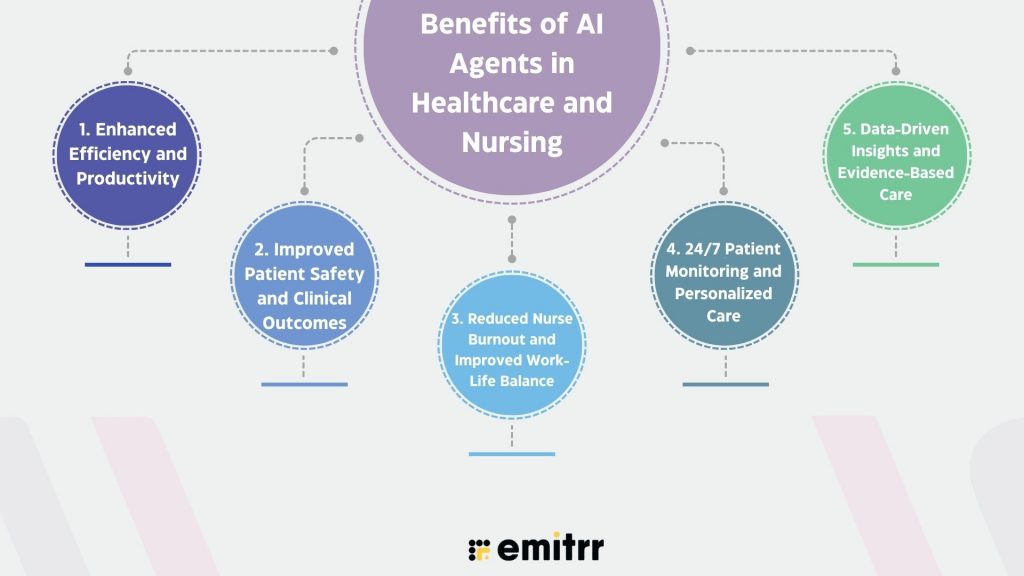
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
AI agents understand and perform administrative tasks, and excel at them. They take the burden off that usually eats into nursing care time. From managing patient scheduling to drafting clinical notes, these AI agents perform 360-degree tasks with precision, speed, and predictive insight. Deloitte reports low-value tasks consume ~15-28% of nurses’ work; AI tools could free up 13-21% of nurses’ time annually (≈ 240-400 hours) by automating admin work.
Consequently, hospitals report smoother workflows, while nurses gain back the precious time they should be investing in actual patient care. For healthcare systems, that translates into better resource use, higher throughput, and cost savings.
2. Improved Patient Safety and Clinical Outcomes
AI agents relentlessly monitor patient data, detect anomalies, and flag when trouble is brewing. AI agents diagnose a rising heart rate or a higher temperature before it becomes critical or life-threatening. They also catch patterns in records or scans that humans might miss, boosting accuracy and reducing errors. The result? Fewer preventable complications and stronger outcomes for patients.
If you’re looking for proof, know that the CONCERN Early Warning System (≈ 60,000 patients) cut mortality risk by 35.6%, reduced sepsis by 7.5%, and shortened hospital stay by ~0.5 days.
3. Reduced Nurse Burnout and Improved Work-Life Balance
The burnout of nurses inside medical establishments has always been a grave problem. Thankfully, AI agents have become instrumental in easing the load. By automating the majority of redundant, complex, and time-intensive tasks, they are freeing nurses to address meaningful care. Teams are leaving work on time more often, morale improves, and turnover drops.
AI scribes in a six-week pilot saw a 40% reduction in reported clinician burnout. In a field where stress levels run high, that support feels essential, not optional.
4. 24/7 Patient Monitoring and Personalized Care
AI agents never tire, never blink, and never stop watching over patients. Always absorbing data from hundreds of wearables and in-room sensors, these agents track vitals continuously and catch problems before they turn into massive issues. Plus, these agents are a driver of personalization. These systems personalize care by pulling in each patient’s history, habits, and risks to guide tailored interventions.
Across many studies, AI-powered monitoring (wearables, real-time alerts) have detected early physiological changes (e.g. fever, pain) before standard methods. Patients have felt watched over, even beyond the hospital walls.
5. Data-Driven Insights and Evidence-Based Care
AI agents turn oceans of clinical data into practical insights and actionable guidance. They analyze patient histories, live monitoring feeds, and the latest research to surface insights that make decisions sharper and faster. Nurses get real-time recommendations fitting best practices, while administrators use aggregated data to refine protocols. The result is care that’s more precise, consistent, and evidence-based.
Early warning models in meta-analysis showed significantly better predictions of adverse events versus traditional methods; trend towards shorter stays and lower mortality.
Disadvantages of AI Agents in Nursing
If you think AI agents in nursing care are all sunshine and rainbows, you’re mistaken. The section gives a glimpse into the top 6 disadvantages of AI in nursing.
1. Data Privacy and Security Risks
AI agents often handle troves of patient data and introduce more integration points, third-party tools, or even cloud services. All this widens the “attack surface” for hackers, leaks, or misuse. Plus, some AI agents fetch or post-process data automatically, taking the lid off from some unexpected vulnerabilities. A recent paper showed that many medical AI agents are vulnerable to adversarial prompts embedded in web pages: attackers could inject false info, manipulate recommendations, or steal conversation logs.
2. Algorithmic Bias and Ethical Concerns
AI agents are only as fair as the data and assumptions behind them. If the training data underrepresents certain groups, or if social/cultural biases are seeping in, AI agents, by the virtue of their fundamental nature, can understate or misrepresent needs. A concrete example that comes to our mind is that of the London School of Economics. It did a study using real social care case notes (617 cases) and generated 29,616 summary pairs by swapping only the gender. The output from Google’s Gemma model repeatedly used more severe descriptors like “disabled,” “unable,” “complex” for male cases, while downplaying similar needs in female ones. That kind of disparity can translate into worse care for certain groups.
3. Integration, Interoperability, and Cost Barriers
Even when AI looks great on paper, getting it to work in a real hospital or clinic setting is often a slippery slope. Legacy systems don’t always play along, data formats are utterly fragmented and disparate, and APIs are inconsistent. Taking the complexities further is the staff that lacks training and an infrastructure plagued by downtime. It’s not just about buying software. It’s a whole process of building pipelines, governance, monitoring, maintenance. One recent survey found that though 80% of healthcare experts believe workflow optimization is a top goal, only ~63% feel their organizations are actually prepared to use GenAI to achieve it. That gap signals how expensive, risky, or labor-intensive full integration tends to be.
4. Resistance to Adoption and Workforce Training Gaps
You can build the best agent in the world, but if nurses, doctors, or support staff don’t trust it, don’t understand what it’s doing, or aren’t trained to identify when it’s wrong, adoption stalls or backfires. There are also concerns about accountability, liability, usability. From a 2025 Wolters Kluwer / Ipsos survey: only 18% of respondents were aware of formal policies around GenAI use in their organizations, and only about 20% had structured training programs. That means most staff are flying blind.
5. Potential Job Displacement and Over-Reliance on AI
AI agents will automate or assist many routine tasks, which is good, but there’s a risk people start leaning too heavily on the AI. That can erode clinician judgment, reduce hands-on skills, or shift the role of nurses in ways some may find threatening. In the same Wolters Kluwer readiness survey, more than 57% of healthcare workers said they believe over-reliance on GenAI might erode clinical decision-making skills. That kind of sentiment matters: if people don’t feel supported, or if tools are overpromised, morale and patient safety are at risk.
6. Lack of Regulatory Clarity and Compliance Standards
Regulation is trying to catch up, but in many places it’s still fuzzy: unclear who’s responsible when an AI agent errs (vendor, hospital, clinician?), what validation is required, how transparency is enforced, how bias is audited, what evidence is needed. Without clear rules, hospitals and nurses may end up exposed legally or ethically. Also, inconsistent standards make scaling difficult: a tool approved in one region mightn’t pass in another. The Wolters Kluwer report shows that only 18% of healthcare professionals know about any formal GenAI policies in their organization, which implies that many AI users may not have oversight or consistent compliance.
AI, Telehealth, and Broader Digital Health in Nursing
Use cases and examples of artificial intelligence in nursing now range from virtual assistants that handle check-ins to multi-layered AI agents that triage symptoms and feed predictions into clinical workflows.
1. Telemedicine and AI-Enabled Remote Patient Care
Telehealth became mainstream during the last wave of change and AI made it stick. AI agents join video visits to summarize conversations, surface red flags, and even guide structured remote exams. For routine follow-ups, agents handle symptom checks and escalate only when a human needs to step in. That means fewer pointless trips to the clinic and more focused nurse time when a problem truly needs hands-on care.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) and Wearable Health Devices
Wearables and bedside IoT sensors feed a nonstop stream of vitals into AI platforms. These agents spot trends that a single snapshot might miss, like creeping oxygen drops or subtle heart-rate shifts, and they ping nurses before the situation becomes urgent. In practice, this turns monitoring into a continuous safety net that works in hospital rooms, rehab centers, and patients’ homes.
3. Data Analytics and Electronic Health Record Integration
AI pulls siloed data together so nurses see the full story faster. Tools now link analytics to electronic health records and push concise, actionable prompts into nursing workflows. Instead of hunting through charts, nurses get nudges about drug interactions, risk of deterioration, or gaps in preventive care. Integrating predictive models into EHRs has become a core strategy for hospitals wanting faster, safer decision making.
How AI Agents Will Transform Nursing Care
Looking ahead, AI in healthcare examples point to a richer, more blended future. The next chapter will be less about replacing people and more about giving teams smarter tools that fit naturally into clinical routines.
1. Emerging Technologies (Advanced Robotics, AR/VR, etc.)
Robots already carry meds and push supply carts; the next generation will assist with physical tasks that strain staff and augment training with immersive AR scenarios. Expect practical robotics to reduce manual lifting and routine walking, while AR helps nurses rehearse complex procedures in lifelike simulations.
2. Human-AI Collaboration and Ethical AI in Nursing
The most useful AI agents will act like team members that know their limits. Nurses will validate and adapt AI suggestions, while governance and design focus on privacy, fairness, and explainability. That human-in-the-loop model keeps clinicians in charge and helps build patient trust. Conversations about consent, bias, and clear escalation rules will shape how broadly AI agents are used across care settings.
3. Long-Term Impact on Patient Experience and Healthcare Delivery
Over time, the promise is simple: care that is more personal, more proactive, and less fragmented. Patients get timely nudges, fewer preventable readmissions, and smoother journeys between home and hospital. For health systems, that translates into better capacity and smarter allocation of staff and beds. As adoption grows, AI agents will stop feeling like add-ons and start feeling like part of the care team, quietly improving outcomes day after day.

Emitrr: Your Gateway to Integrating AI Into Nursing Care
All pumped up about integrating AI into nursing workflows? Try our advanced yet simple-to-adopt AI agent called Emitrr.
Built with a lot of thought and precision, Emitrr is designed to help medical practices leverage an AI employee that never sleeps, gets the grunt work done, and allows nurses the time it takes to deliver personalized care.
Our tool sends smart reminders that cut no-shows, handles online scheduling to slash booking calls, and gathers intake via digital forms into a single inbox. Team messaging and secure callbacks speed coordination, while integrations with 500+ CRMs let data flow back into existing systems. It scales from solo practices to busy hospitals and adapts to each workflow, turning fragmented admin into a smooth, automated engine that keeps patients engaged and reduces administrative friction.
What’s more? Well, a lot about it is covered in the five pointers below. Give a good read!
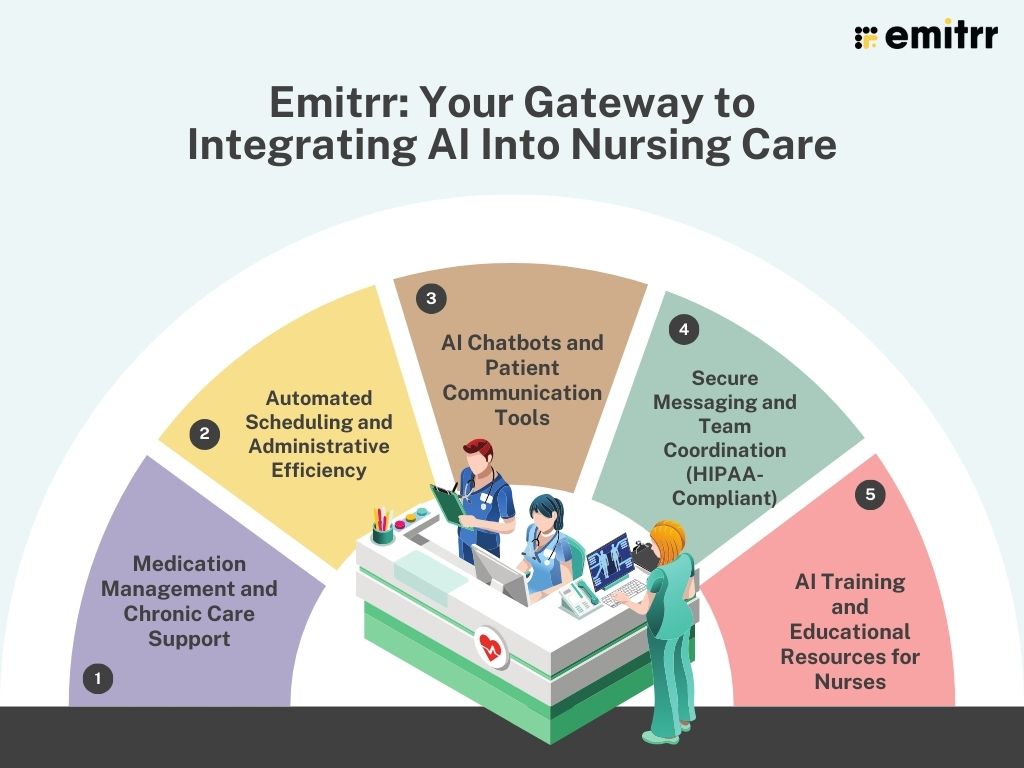
1. Medication Management and Chronic Care Support
Emitrr helps clinics keep medication schedules tight and chronic care manageable. AI agents send personalized med reminders, confirm refill needs, and surface adherence issues to nurses before they become problems. For chronic patients, the system tracks symptoms over time and flags worsening trends so care teams can step in early. That reduces avoidable admissions and keeps long-term care plans on track.
2. Automated Scheduling and Administrative Efficiency
Emitrr automates patient bookings, fills open slots, and pings no-shows with friendly reminders. It also integrates with clinic calendars to reduce double bookings and cut down on manual phone tag. The net effect is fewer empty slots, less front-desk stress, and more time for nurses to do clinical work instead of admin work.
3. AI Chatbots and Patient Communication Tools
Emitrr’s chatbots and voice AI handle routine patient questions, triage simple symptoms, and run appointment confirmations. They speak in everyday language and hand off anything complex to a human. That keeps patients satisfied and reduces the back-and-forth that usually ties up nursing staff. The chat tools also make it easy to push targeted education and follow-up messages at scale.
4. Secure Messaging and Team Coordination (HIPAA-Compliant)
Emitrr provides encrypted texting, audit trails, and role-based access so teams can share results, notes, and urgent alerts without risking patient privacy. That means faster handoffs, clearer team threads, and one place for clinical conversations that used to be scattered across apps and sticky notes.
Help nurses manage patient calls with clear, friendly voicemail greetings. Download professionally written scripts today.

5. AI Training and Educational Resources for Nurses
Emitrr also supports upskilling and elevating the fundamental expertise of the staff. The platform offers practical courses and bite-sized modules that teach nurses how to work with AI agents, interpret predictive alerts, and use new communication tools safely. Training helps staff trust the tech and adopt it faster, turning potential disruption into a clear advantage for patient care.
FAQs
AI’s being put to multiple uses in nursing, making hospital workflows smoother than ever. The technology is helping with routine triage, medication reminders, remote monitoring, drafting notes, and smart scheduling. It flags risks early and automates repetitive workflows so nurses can focus on hands-on care.
The biggest benefits of AI in healthcare are precision and proactiveness of care. Teams are able to deliver care at scale, speed, and without operational roadblocks. Instead of acting on what’s happening currently, it’s also helping predict what’s coming ahead and taking remedial steps. So, faster identification of risk, fewer avoidable readmissions, time savings from automation, better patient engagement, and improved team coordination.
AI isn’t free of its drawbacks, unfortunately. When given absolute freedom, it can work as a foe instead of a friend. AI can introduce false alerts, require workflow redesign, and raise privacy and bias concerns. Good governance and human oversight are essential.
Absolutely not. AI can’t replace the cerebral and emotional intelligence that nurses possess and drive a difference with. AI can handle repetitive work and augments clinical judgment, but nurses are and will forever remain central to assessment, empathy, and final decision making.
Resistance to AI is normal. Nurses might find themselves walking on thin ice with AI doing the maximum of their work – faster. But it’s important to understand that AI currently lacks the genuine emotional intelligence (EI) to provide true empathy, intuition, and deep understanding of human emotions. Nurses can take to AI as a friend and learn how to read AI alerts, practice human-in-the-loop workflows, take available training, and speak up about how AI fits into clinical routines.
Automated appointment reminders and chatbots for patient queries, wearables linked to AI agents for continuous monitoring, AI-driven scheduling, and HIPAA-compliant secure texting that streamlines team coordination. Emitrr packages these capabilities into easy-to-deploy tools for clinics and small hospitals.
Conclusion
AI in healthcare means fewer routine phone calls, faster documentation, and safer handoffs. For patients, it means quicker access, clearer instructions, and more personalized follow-up outside the hospital. That said, AI is an assistant, not a replacement. Human judgment remains essential. Teams must guard against disadvantages of AI in healthcare like bias, protect patient privacy, and design clear escalation rules so clinicians stay in control.
Emitrr turns tedious admin into background work without trespassing – and helps nurses spend more time with patients. If you’re curious to know how it can help you, see Emitrr in action.

 4.9 (400+
reviews)
4.9 (400+
reviews)
