Introduction
When your physician discusses a diagnosis with you over the phone, most are unaware that the voice data itself is Protected Health Information (PHI). The moment a patient or healthcare provider communicates via phone call, voicemail, or text, that conversation becomes a compliance risk once it is transferred over a digital line. This is where HIPAA-compliant VoIP systems come into play as communication tools, but more importantly as a ‘security framework’ which determines if a healthcare organization remains compliant or penalized.
HIPAA-compliant VoIP phone systems incorporate end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), audit trails, access controls, and BAAs, which provide organizations with compliant, traceable, and secure communication. As the healthcare ecosystem moves toward telehealth and hybrid work models, procuring a HIPAA-compliant VoIP solution is no longer an option, but a strategic requirement for organizations.
What Is HIPAA-Compliant VoIP?
A HIPAA-compliant VoIP is a secure VoIP for healthcare and medical communities that meets all HIPAA requirements for protecting PHI (Protected Health Information). In contrast to consumer-level calling applications (e.g., Skype or WhatsApp), a HIPAA-compliant VoIP service incorporates superior standards of encryption, strictly enforced authentication protocols, and extensive administrative controls to ensure not only secrecy but also audibility of the voice communications.
A HIPAA-compliant VoIP system does more than just encrypt calls; it protects voicemail, call recordings, and, potentially, SMS. A VoIP system must provide:
- VoIP data-in-transit encryption (the PHI is encrypted while in transfer).
- VoIP data-at-rest encryption (the PHI is secured while in storage of audio or text data).
- VoIP audit trail PHI logging, which tracks access or logging while those logs are logged.
- VoIP user access control and role-based access to VoIP permissions.
- VoIP regulations to ensure that call recording is stored and managed in a HIPAA safe environment.
- A VoIP BAA (Business Associate Agreement) must be signed with the provider.
Why HIPAA compliance matters for VoIP Every call made in healthcare can have electronic PHI (ePHI) in the call, lab results, prescriptions, billing, diagnosis, etc. Without VoIP HIPAA compliance, the call can be intercepted, monitored, leaked, or worse, not be used for the purpose that the provider intended.
Having a VoIP system that is HIPAA compliant means that:
- Voice and text data are encrypted (both in motion and at rest).
- Only authorized users may have access to communication through VoIP with MFA for users.
- VoIP Audit trail PHI reports provide record-keeping transparency for compliance audits.
- PHI can be altered or deleted without logging it (VoIP with audit logs).
- Service providers share the responsibility with you with a VoIP BAA agreement.
- For the organization, this means fewer data breaches, less liability, and compliance with the HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules.
VoIP Communication Channels Covered Under HIPAA
HIPAA compliance includes more than just the spoken voice on a call. The use of VoIP’s unified digital platform means many channels of communication that use the VoIP system may transmit and/or store ePHI. Therefore, all of these channels sit under the scope of HIPAA security compliance. The important channels that a comprehensive healthcare VoIP-compliant solution will need to secure include:
- Voice Calls: Any spoken exchange that contains patient identifiers or medical information.
- VoIP Call Recording: Any stored voice logs that are utilized for verification or quality assurance must stay HIPAA safe.
- Voicemail: VoIP will require secure voicemail and voicemail storage encryption.
- Text Messaging (SMS / MMS): VoIP with a secure SMS/messaging protocol falls into the coverage of HIPAA, and would need to be encrypted and authenticated.
- Video Calls: Video calls will need to utilize end-to-end encryption VoIP protocols while used for telehealth.
- Fax-over-IP or VoIP Fax: Fax-over-IP or VoIP fax communication will have the same HIPAA VoIP archiving & backup rules as other PHI channels.
Across all these VoIP communication channels, HIPAA compliance isn’t limited to encryption and storage alone. It also depends on how messages are delivered when calls go unanswered. Using clearly written, HIPAA-compliant voicemail scripts helps ensure patient communication stays professional and privacy-safe without exposing sensitive information.
Access ready-to-use HIPAA-compliant voicemail scripts for healthcare teams.

Risks and Consequences of Non-Compliance
Employing a VoIP system that does not comply with HIPAA regulations can be devastating for healthcare providers. Non-HIPAA VoIP risks include:
- Data Breaches: Exposure of PHI due to unprotected calls or messages.
- Fines: A violation penalty of $100 to $50,000, with a cap of $1.5M per year.
- Loss of Reputation: A patient will lose trust after sensitive health information is exposed.
- Legal Action: Class-action lawsuits or regulatory HIPAA compliance audits.
- Operational Downtime: Audits and suspensions of operational capacities or systems.
Non-HIPAA compliant VoIP risks are not only imposed on large hospitals. Even a solo doctor forwarding patient phone calls to their personal phone number without a VoIP in place to restrict access to PHI is a violation of HIPAA compliance.
HIPAA Rules for VoIP
To comply with Medical VoIP HIPAA regulations, we need to adhere to the main rules that specify the security and use of electronic protected health information (ePHI). The HIPAA Security Rule is the prevailing rule that outlines three domains of safeguards that need to be present for the VoIP system.
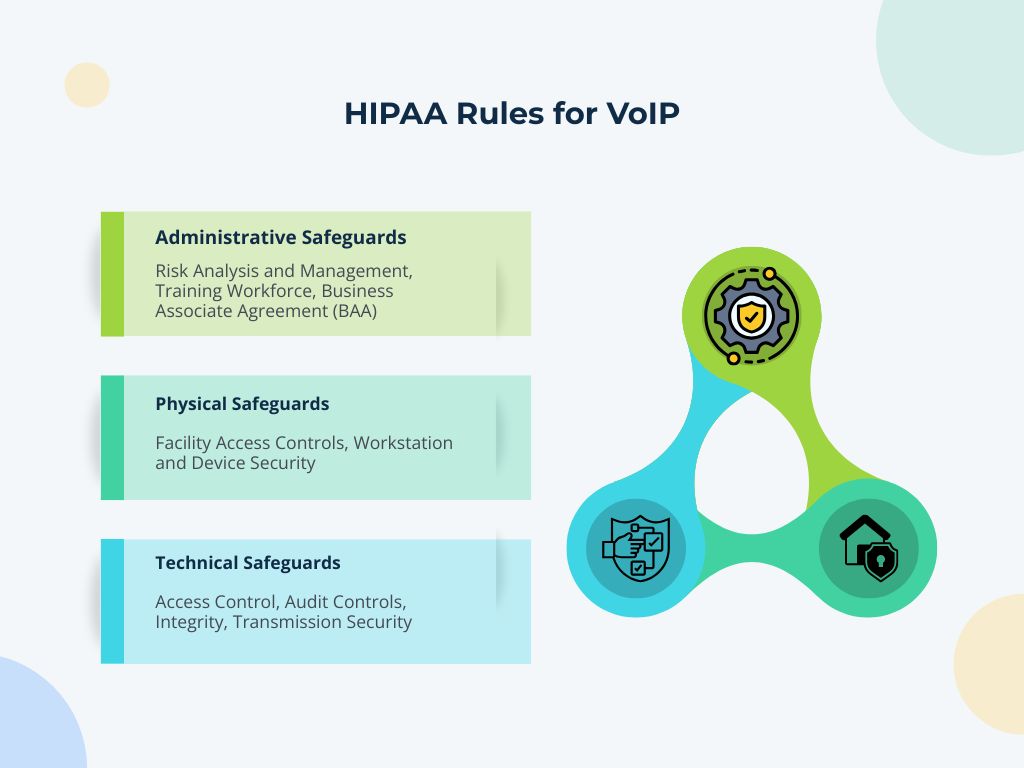
1. Administrative Safeguards
These are the management, policy, and procedure-related obligations to selecting, developing, implementing, and maintaining security measures.
- Risk Analysis and Management: Routine, comprehensive risk assessments of the VoIP system to identify vulnerabilities and threats to ePHI.
- Training Workforce: Ensuring that all employees have a formalized (preferably written) training policy and procedure that indicates their roles and responsibilities in using HIPAA-compliant VoIP service, handling PHI, and security requirements.
- Business Associate Agreement (BAA): Obtain a VoIP BAA completed and signed by the VoIP provider, stating that they will maintain HIPAA safeguards for all PHI they create, receive, maintain, or transmit on behalf of the covered entity.
2. Physical Safeguards
These are the measures to protect the physical electronic systems and related equipment, storing/ePHI from unauthorized access, damage, or interference.
- Facility Access Controls: Physical access to the server room/data center that houses any on-premises (in-house) VoIP equipment/data-at-rest is restricted.
- Workstation and Device Security: Implementing policies for the secure management and securing all devices (softphones, desk phones, and mobile devices) that will access the HIPAA-compliant VoIP phone system.
3. Technical Safeguards
These are the technology-based security processes in place to secure ePHI and to control and monitor access to ePHI. Most of the specific VoIP features to ensure compliance will reside in this safeguard.
- Access Control: Implementation of unique user IDs, procedures for emergency access, and most importantly, VoIP identity authentication and VoIP user access control to ensure that only authorized personnel can access PHI, especially ePHI, in any hardware, software, provider, or environment. VoIP multi-factor authentication (MFA) for users will be a critical part of controls here.
- Audit Controls: Implementation of mechanisms, including VoIP with audit logs, to record and examine activity in any system, for example, who accessed what data and at what time, all of which are critical when forensic analysis is necessary.
- Integrity: Policies and procedures that will protect ePHI from inappropriate alteration or destruction, for example, securing file storage for call recordings.
- Transmission Security: Using end-to-end encryption, VoIP adds encryption measures to mitigate unauthorized access to ePHI when it is in transit, over the data network, and includes VoIP data-in-transit encryption.
How to Ensure HIPAA Compliance – Best Practices
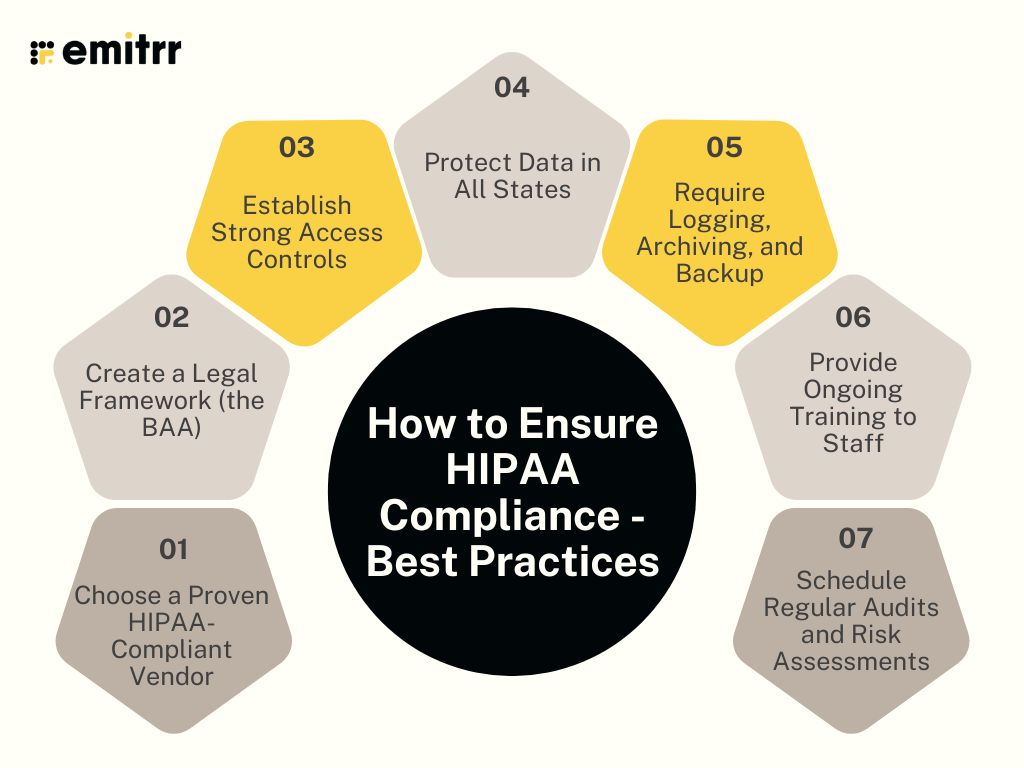
Transitioning from being non-compliant to utilizing a compliant HIPAA VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) solution involves a series of systematic processes. Transitioning involves some due diligence, technical setup, and controls, as well as keeping vigilant after the transition.
1. Choose a Proven HIPAA-Compliant Vendor
The first and most important step in your process is to partner with a telecom services provider that has expertise in healthcare VoIP-compliant solutions and is willing to sign a VoIP business associate agreement (BAA). It should be noted that while this paragraph is not assuming they are, you should obtain proof of their internal security controls, if they do exist, and past audits. A qualified vendor should already have the technical safeguards built in.
2. Create a Legal Framework (the BAA)
Execute the BAA with your chosen provider as soon as possible. The BAA establishes the responsibilities of the healthcare organization (the “covered entity”) and the VoIP service provider (the “business associate”) related to the protection of PHI.
In other words, with the BAA, your VoIP vendor agrees to properly:
- Provide VoIP data-at-rest encryption and VoIP data-in-transit encryption across all communications.
- Maintain a VoIP audit trail PHI log and secure backup for compliance audits.
- Limit who can access PHI via role-based access VoIP and VoIP user access control.
- Notify you of breaches immediately and cooperate during a VoIP compliance audit HIPAA review.
- Ensure that their subcontractors also comply with HIPAA’s security, privacy, and breach notification requirements.
No BAA equals no legal use of that provider’s service to protect and/or communicate PHI, regardless of how great the system is at encrypting the data or providing other security protocols. The BAA is your organization’s legal shield that establishes liability and accountability between both parties for protecting patient data.
3. Establish Strong Access Controls
Leverage the capabilities of the system to ensure the principle of “minimum necessary access” is followed at all times.
- Role-Based Access: Create Role-based access VoIP policies so that a front-desk receptionist may only have access to VoIP call logs; a clinician may access secure voicemail, and only an administrator may access VoIP access control to configure PHI settings in a VoIP application.
- Authentication: Require strong passwords, regularly change passwords, and use VoIP MFA users at each access point (desk phone, softphone, mobile app) to establish and authenticate VoIP identity.
4. Protect Data in All States
Ensure the provider is encrypting data in transit and at rest appropriately.
- In Transit: Calls and messages must be secured with end-to-end encryption, VoIP protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP). This is data in transit encryption for VoIP.
- At Rest: Data stored like voicemails, secure chat history, VoIP call recording, HIPAA safe files must be secured by VoIP data at rest (ex., AES-256).
5. Require Logging, Archiving, and Backup
Use appropriate structures to hold people accountable and restore order during a disaster.
- Audit Trails: Enable VoIP with audit logs or a VoIP audit trail, as appropriate. Review regularly to see every access, change, or transmission of PHI. Logging for HIPAA compliance is necessary and also required for breach investigation.
- Retain and Back Up: Have HIPAA VoIP archiving & backup policies that follow state and federal medical record retention laws. Ensure the archive and backup are encrypted and tested regularly.
6. Provide Ongoing Training to Staff
Technology is only as secure as the individual utilizing it. Employees must have training related to secure, HIPAA-compliant VoIP service use, risks of using personal devices, and procedures for handling voicemails and recorded calls containing PHI.
7. Schedule Regular Audits and Risk Assessments
Compliance is an ongoing process, not just an initial effort. Incorporate regular VoIP compliance audit, HIPAA, and risk assessments to address any new VoIP security risks HIPAA that might be introduced through system upgrades, new features added, or changes in workflows.
Ensure HIPAA Compliance with Emitrr
Emitrr offers a HIPAA-compliant VoIP phone system that is built specifically for providers and other regulated industries. The system delivers AI automation, end-to-end security, and compliance communication tools, ensuring a seamless, protected environment for voice and text.
Some of Emitrr’s HIPAA VoIP features include:
- End-to-End Encryption VoIP: Emitrr makes certain that every use case for calls, voicemails, and text messaging is fully encrypted from sender to receiver, with encryption that prevents interception or tampering. This VoIP end-to-end encryption capability ensures that PHI is safeguarded during all methods of communication.
- Role-Based Access & VoIP User Access Control: Access to sensitive data is limited using role-based access VoIP permissions, meaning that only authorized staff can see or handle PHI. Admins can simply define access permissions for clinicians, front-desk teams, and administrators.
- VoIP MFA for Users: Emitrr adds a layer of multi-factor authentication (MFA) for users at the time of log-in, to verify user identity beyond the password. This VoIP for user MFA protection ensures that even if a user’s credentials were compromised, unauthorized access would not be possible.
- VoIP Audit Trail PHI & Secure Logging: Every interaction, calls, messages, voicemails, are logged using a detailed VoIP audit trail for PHI. This audit trail provides complete visibility of interactions by logging what data was accessed, by whom, when, and what steps may have taken place. This visibility provides simplicity when conducting compliance audits.
- VoIP Encryption for Data at Rest & Data in Transit: Emitrr uses VoIP data-at-rest and VoIP data-in-transit encryption to ensure that the data is unreadable regardless if at rest on a server or in transit via a network. This two-layered approach provides full PHI privacy and security.
- HIPAA VoIP Archiving & Backup: With HIPAA VoIP archiving and backup, you can automatically archive call logs, messages, and recordings at the same time. All backups maintain encryption and are secured according to the retention policies of HIPAA, which attest that the information is never lost or mishandled.
- VoIP with Secure SMS/Messaging & Secure Voicemail: Emitrr combines communication by utilizing secure SMS/messaging and VoIP with secure voicemail. The platform enables clinics and healthcare professionals to communicate updates, reminders, and follow-ups with patients and stakeholders, using encrypted SMS messaging features and VoIP to keep things HIPAA compliant and secure.
- Signed BAA: Emitrr will sign a VoIP BAA with all healthcare clients which will clearly define the joint responsibilities we will validate ou roles in protecting ePHI (Electronic Protected Health Information) for you and your organization. This agreement will legally bind Emitrr to HIPAA compliance for the safekeeping of ePHI with the clients responsibilities to hiring a HIPAA compliant VoIP provider and further protects Emitrr from liability once signed and agreed upon.
- Technical Safeguards: Emitrr uses end-to-end encryption VoIP for every conversation, and is supported with encryption for all VoIP data-at-rest, including recordings and voicemails to further protect this stored and continuing data as a reminder of the care provided to your patients. These technical safeguards ensure Emitrr is a HIPPA ready VoIP partner you can trust with secure communication for healthcare.
Whether it’s appointment reminders, teleconsults, or patient follow-ups, Emitrr’s secure VoIP for healthcare brings it all together under one compliant, AI-enriched solution, truly the most reliable VoIP HIPAA solution of 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: A HIPAA-compliant VoIP uses encryption, access control, logs all activity, and has a signed VoIP BAA to share compliance responsibility.
Ans: Yes, if the system is a VoIP call recording HIPAA safe system, that encrypts the recordings and stores the recordings securely with limited access.
Ans: Only if the vendor agrees to a VoIP BAA, and has VoIP data-in-transit encryption and VoIP MFA for users. If not, it is a VoIP non-HIPAA-compliant system.
Ans: Penalties for violating HIPAA with VoIP include fines of up to $50,000 per violation, and damage to reputation for any exposure of PHI.
Ans: Yes. Emitrr operates VoIP with secure SMS/messaging and VoIP with secure voicemail, both encrypted and HIPAA authorized.
Conclusion
As voice and text take center stage as communication modalities with patients, adopting a HIPAA-compliant VoIP system is not only a best practice; it is a requirement. Many VoIP providers implement identity authentication, audit logging, access controls, and encryption for VoIP, allowing for PHI to be safeguarded while trust with patients is maintained and assuring practitioners operate safely while HIPAA compliant.
Emitrr’s HIPAA-compliant VoIP phone system enables clinics, hospitals, or multi-location networks to communicate securely but seamlessly by merging security with convenience.
Book a demo with Emitrr today and learn how to ease compliance while enhancing patient communication using a HIPAA-ready VoIP solution built for today’s healthcare ecosystem.

 4.9 (400+
reviews)
4.9 (400+
reviews)

